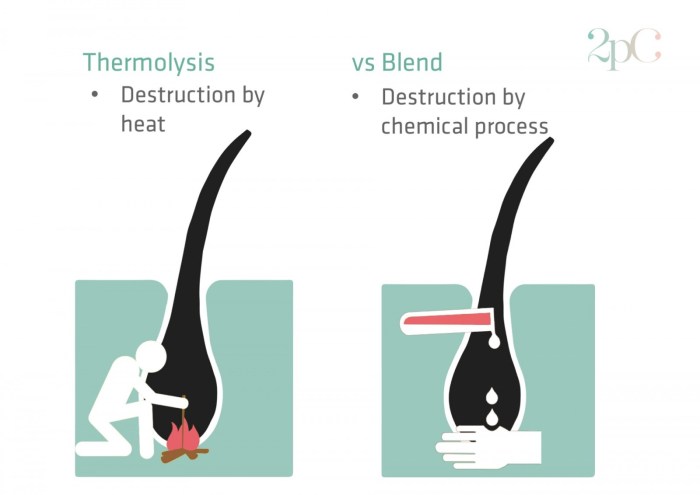
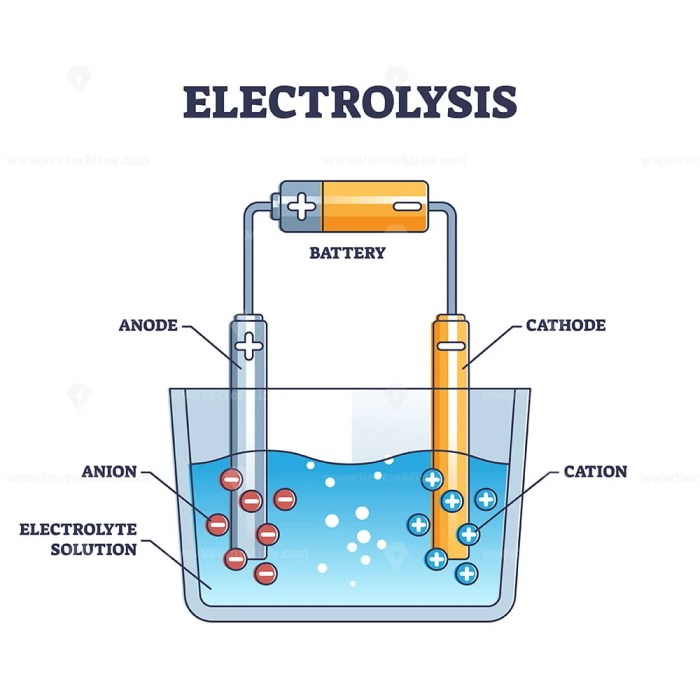
The thermolysis method of electrolysis is also called the: is an electrolysis technique that utilizes heat to break down compounds. This process involves the application of high temperatures to induce chemical reactions, offering unique advantages and applications in various industries.
The thermolysis method has a rich history, dating back to the early days of electrochemistry. Over the years, it has been refined and modified to enhance its efficiency and versatility. Today, it finds applications in diverse fields such as materials science, environmental remediation, and chemical synthesis.
1. Thermolysis Method Overview
The thermolysis method of electrolysis is an electrochemical process that utilizes heat to break down compounds. This technique involves passing an electric current through a substance while simultaneously exposing it to high temperatures, typically ranging from 500 to 1500 degrees Celsius.
The thermolysis method relies on the principle that heat can provide the activation energy necessary to initiate the breakdown of chemical bonds. By applying both heat and an electric current, the energy barrier for bond dissociation is reduced, allowing the compounds to decompose more readily.
Helpful Answers: The Thermolysis Method Of Electrolysis Is Also Called The:
What are the key advantages of the thermolysis method?
The thermolysis method offers several advantages, including high efficiency, selectivity, and versatility. It can break down complex compounds into simpler molecules, making it useful in various industries.
What are the limitations of the thermolysis method?
The thermolysis method has some limitations, such as the potential for side reactions and the need for high temperatures. However, these limitations can be mitigated by optimizing the process conditions.
What are some common applications of the thermolysis method?
The thermolysis method has applications in various industries, including materials science, environmental remediation, and chemical synthesis. It is used to break down organic compounds, purify materials, and synthesize new chemicals.