Embark on a musical odyssey with the C# fully diminished 7th chord, a harmonic enigma that tantalizes the ears and challenges the intellect. This chord, a cornerstone of jazz and classical music, possesses a haunting beauty and a versatility that belies its complex construction.
Delve into its intricate structure, unravel its harmonic functions, and explore its captivating voicings. Discover how this chord interacts with others, creating harmonic progressions that evoke both tension and resolution. Join us as we dissect the C# fully diminished 7th chord, unlocking its secrets and revealing its immense musical potential.
Fundamentals of C# Fully Diminished 7th Chord
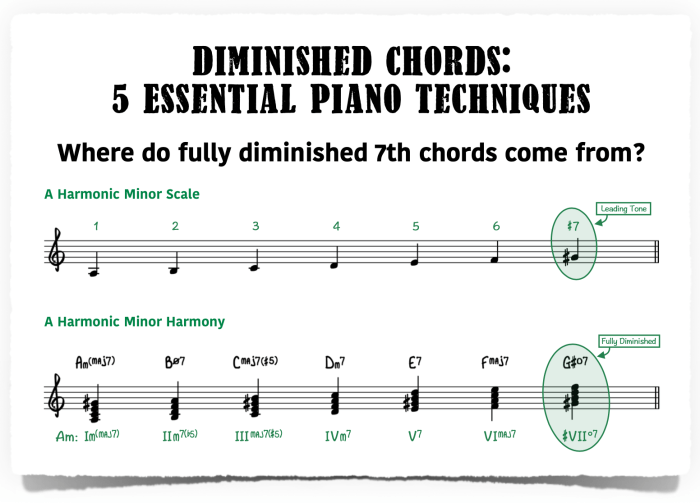
The C# fully diminished 7th chord, denoted as C#dim7, is a dissonant chord that consists of four notes: the root (C#), a minor third (E), a diminished fifth (G), and a diminished seventh (B♭). Its structure can be summarized as 1 – b3 – b5 – bb7.
In terms of harmonic function, the C#dim7 chord typically serves as a pre-dominant chord, leading to a dominant chord and ultimately resolving to the tonic. It creates a sense of tension and instability, often used to build anticipation or add a touch of dissonance to a musical passage.
Intervals and Structure
The C# fully diminished 7th chord is built upon the root note C#, with intervals of a minor third (3 semitones) to E, a diminished fifth (6 semitones) to G, and a diminished seventh (9 semitones) to B♭. This unique combination of intervals gives the chord its characteristic dissonant and unstable sound.
Common Uses
The C#dim7 chord is commonly employed in various musical genres, including jazz, classical, and popular music. It is often used:
- As a pre-dominant chord, leading to a dominant chord and resolving to the tonic.
- To create tension and dissonance in a musical passage.
- As a passing chord, connecting two other chords.
- In voice leading, to create smooth voice movements.
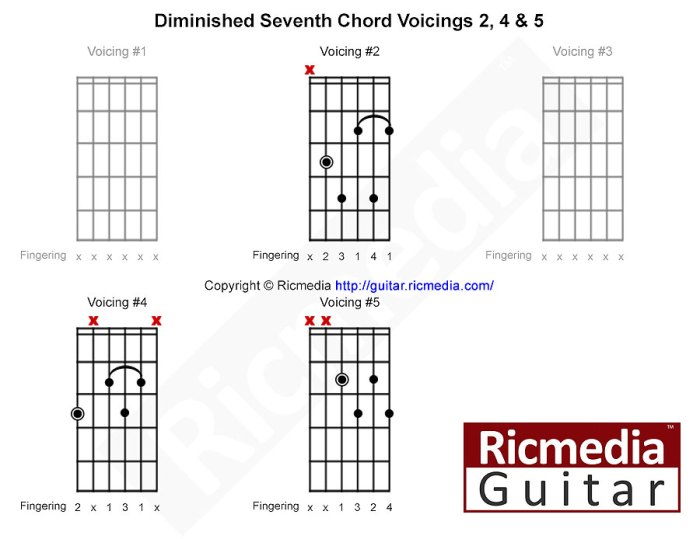
Voicings and Inversions
The C# fully diminished 7th chord can be voiced in various ways, each with its unique sound and harmonic implications. The chord’s inversions, which involve reordering the notes within the chord, also affect its character.
Root Position Voicing
In root position, the root (C#) is the lowest note in the chord. This voicing emphasizes the fundamental pitch of the chord and provides a stable harmonic foundation.
First Inversion Voicing
In first inversion, the third (E) becomes the lowest note. This voicing creates a more dissonant sound and suggests movement towards the dominant chord. It is often used in jazz and classical music.
Second Inversion Voicing
In second inversion, the fifth (G) becomes the lowest note. This voicing has a more open and airy sound, with less emphasis on the root. It is commonly used in suspended chords and extended harmonies.
Third Inversion Voicing
In third inversion, the seventh (B) becomes the lowest note. This voicing has a tense and unresolved sound, often used to create anticipation or suspense. It is commonly found in classical music and jazz.
Harmonic Progressions
The C# fully diminished 7th chord plays a crucial role in various harmonic progressions, often lending a sense of instability and resolution. Its function within these progressions can vary depending on the context.
Resolving to the Tonic
One common progression involving the C# fully diminished 7th chord is its resolution to the tonic, or I chord. In this context, the diminished chord acts as a predominant, creating tension that resolves to the stability of the tonic.
Example: C#dim7
- F#7
- Bm7b5
- Emaj7
As a Secondary Dominant
The C# fully diminished 7th chord can also function as a secondary dominant, leading to a chord other than the tonic. This progression adds harmonic interest and can create a sense of anticipation.
Example: Gmaj7
- C#dim7
- F#m7b5
- Bm7b5
- Emaj7
In Minor Keys
In minor keys, the C# fully diminished 7th chord can be used as a substitute for the V chord, providing a more dissonant and unresolved sound. This substitution adds depth and complexity to minor key progressions.
Example: Am7
- Dm7
- G7
- C#dim7
- Fmaj7
Applications in Music
The C# fully diminished 7th chord, with its dissonant and unstable sound, is a powerful tool for creating tension and resolution in music. Its applications span various genres and styles, from classical to jazz and contemporary music.
Classical Music
In classical music, the C# fully diminished 7th chord is often used in chromatic progressions, where it serves as a transitional chord between keys. It can also be found in cadences, adding a sense of drama and anticipation before the final resolution.
The C# fully diminished 7th chord, with its distinctive dissonance, can evoke a sense of tension and unease. It’s a versatile chord that can be found in various musical genres. If you’re looking for more insights into the complexities of English grammar, I highly recommend checking out the comprehensive resource on voyages in English grade 8 . This guide provides an in-depth exploration of various grammatical concepts, making it an invaluable resource for students and language enthusiasts alike.
Returning to our discussion of the C# fully diminished 7th chord, its use can add a touch of harmonic intrigue to your compositions.
For example, in Mozart’s “Piano Sonata No. 11 in A Major,” the C# fully diminished 7th chord appears in the development section, creating a moment of harmonic tension before the recapitulation.
Jazz
In jazz, the C# fully diminished 7th chord is a staple of bebop and modal jazz. It is frequently used as a substitute for the dominant 7th chord, creating a more complex and sophisticated sound. The chord’s dissonant nature allows it to resolve to multiple chords, making it a versatile tool for improvisation.
For example, in Miles Davis’ “So What,” the C# fully diminished 7th chord is used extensively throughout the composition, providing a harmonic foundation for the improvisations.
Contemporary Music
In contemporary music, the C# fully diminished 7th chord is often used for its dissonant and experimental qualities. It can be found in atonal and serial music, as well as in film scores and electronic music. For example, in Krzysztof Penderecki’s “Threnody for the Victims of Hiroshima,” the C# fully diminished 7th chord is used to create a sense of chaos and despair.
Comparison with Other Diminished Chords
The C# fully diminished 7th chord shares similarities and differences with other types of diminished chords, such as the half-diminished and diminished 9th chords. Understanding these relationships helps us comprehend the unique characteristics and harmonic functions of each chord.
Half-Diminished Chord
The half-diminished chord is constructed by lowering the 5th of a minor triad by a semitone. Compared to the C# fully diminished 7th chord, the half-diminished chord lacks the lowered 7th, resulting in a less dissonant sound. Its harmonic function is often as a substitute for the dominant 7th chord, resolving to the tonic.
Diminished 9th Chord, C# fully diminished 7th chord
The diminished 9th chord extends the fully diminished 7th chord by adding a lowered 9th. This creates a more complex and dissonant sound. Its harmonic function is often as a substitute for the dominant 9th chord, resolving to the tonic.
However, the diminished 9th chord can also be used as a standalone chord with its own unique tension and release qualities.
Advanced Techniques: C# Fully Diminished 7th Chord
Beyond basic applications, the C# fully diminished 7th chord offers advanced techniques that expand its harmonic possibilities. These techniques delve into the intricate relationships between chords, enhancing musical tension and resolution.
Tritone Substitution
Tritone substitution involves replacing a dominant 7th chord with a diminished 7th chord that shares a tritone interval. For instance, in the key of C, the dominant 7th chord G7 can be substituted with the C# fully diminished 7th chord.
This substitution creates a chromatic alteration that adds tension and resolves back to the original chord, enriching the harmonic progression.
Chromatic Mediant Relationships
Chromatic mediant relationships utilize the C# fully diminished 7th chord as a pivot chord between two chords that are a semitone apart. This technique creates a sense of instability and harmonic motion. For example, in the key of C major, the progression C – C# fully diminished 7th – D minor introduces chromaticism and enhances the harmonic journey.
Creative Exercises
To foster exploration and creative application of the C# fully diminished 7th chord, consider incorporating the following exercises and activities:
Encourage musicians to experiment with the chord’s dissonant and unresolved nature by composing melodies and chord progressions that utilize its tension-building qualities.
Compositional Exploration
- Compose short musical passages that feature the C# fully diminished 7th chord as a primary or secondary chord.
- Experiment with different voicings and inversions of the chord to create varied harmonic textures and melodic possibilities.
- Explore the use of the chord in both major and minor keys, noting its contrasting effects and expressive potential.
Improvisational Activities
- Incorporate the C# fully diminished 7th chord into improvisation exercises, encouraging musicians to explore its melodic and harmonic possibilities in real-time.
- Use the chord as a starting point for improvisation, allowing musicians to navigate its dissonant intervals and resolve them creatively.
- Encourage musicians to experiment with different rhythmic and melodic approaches to the chord, discovering its versatility and adaptability.
Analytical Listening
- Provide recordings or examples of music that effectively utilizes the C# fully diminished 7th chord.
- Encourage musicians to analyze the chord’s usage, harmonic context, and overall effect on the music’s mood and atmosphere.
- Discuss the different ways composers and musicians have employed the chord throughout music history, highlighting its expressive capabilities.
FAQ Insights
What is the structure of a C# fully diminished 7th chord?
It comprises the notes C#, E, G, and Bb, forming a stack of minor thirds.
How is the C# fully diminished 7th chord commonly used in music?
It often appears in jazz and classical compositions to create tension, resolve dissonances, and add harmonic complexity.
What is a tritone substitution involving the C# fully diminished 7th chord?
It is a technique where the C# fully diminished 7th chord is used as a substitute for a dominant 7th chord a tritone away, such as the F#7 chord.