Nursing care plan for ect – Embarking on a journey through the intricate world of nursing care plans for electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), we unravel the essential elements that shape this specialized healthcare approach. Dive into a comprehensive exploration of assessment techniques, interventions, monitoring strategies, and ethical considerations, gaining a profound understanding of ECT’s role in patient care.
Throughout this guide, we will navigate the complexities of ECT, empowering nurses with the knowledge and skills to provide compassionate and effective care. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of this therapeutic modality, ensuring optimal outcomes for patients undergoing ECT.
Nursing Assessment
A comprehensive nursing assessment is essential for patients undergoing ECT to ensure their safety and optimize treatment outcomes.
The assessment process involves gathering information about the patient’s physical, psychological, and social status.
Physical Assessment
- Vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, temperature)
- Physical examination (skin, head, neck, chest, abdomen, extremities)
- Neurological examination (mental status, reflexes, coordination)
- Laboratory tests (blood work, urinalysis)
Psychological Assessment
- Mental health history (past and present diagnoses, treatments, medications)
- Current symptoms (mood, anxiety, cognitive function)
- Suicide and homicide risk assessment
- Use of standardized assessment tools (e.g., Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, Beck Depression Inventory)
Social Assessment
- Social support system (family, friends, significant others)
- Living situation and financial status
- Occupational and educational history
- Cultural and religious beliefs
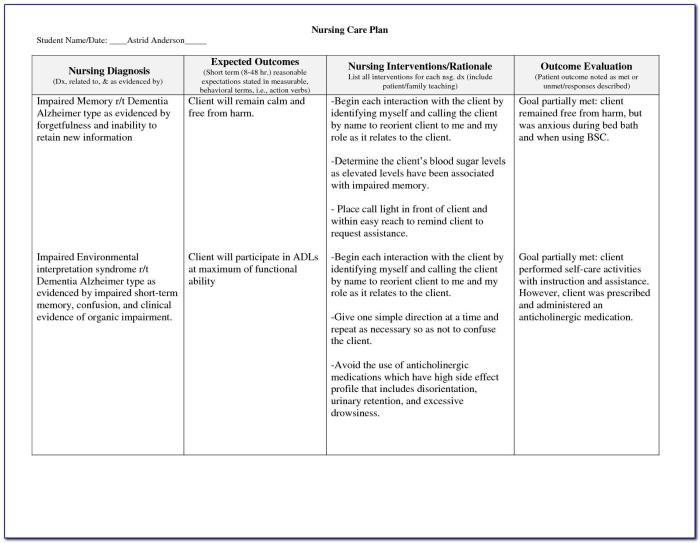
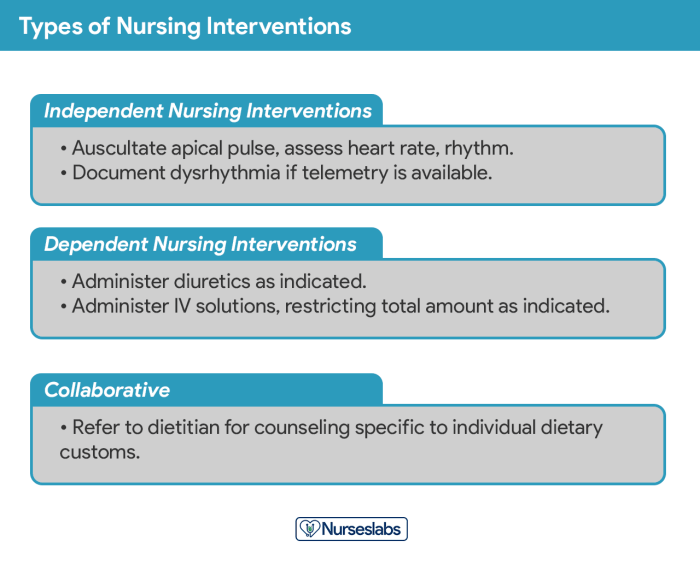
Nursing Interventions
Nursing interventions for patients undergoing ECT aim to ensure their safety, comfort, and well-being throughout the procedure and recovery phase. These interventions are crucial in minimizing potential risks and optimizing treatment outcomes.
The primary nursing interventions for patients undergoing ECT include:
Pre-ECT Interventions
- Obtaining informed consent:Ensuring that the patient fully understands the procedure, its benefits, and potential risks, and has voluntarily consented to the treatment.
- Assessing the patient’s physical and mental health:Conducting a comprehensive medical history and physical examination to identify any contraindications or potential complications.
- Preparing the patient for the procedure:Providing clear instructions on fasting, sedation, and any other pre-procedure requirements.
- Establishing a supportive and safe environment:Creating a calm and reassuring atmosphere, providing comfort measures, and ensuring the patient’s privacy.
During ECT Interventions
- Monitoring the patient’s vital signs and neurological status:Continuously monitoring the patient’s heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and neurological responses during the procedure.
- Providing emotional support and reassurance:Staying with the patient throughout the procedure, offering comfort, and addressing any concerns or anxieties.
- Administering medications as prescribed:Giving medications to induce sedation, muscle relaxation, and prevent seizures as per the physician’s orders.
- Protecting the patient from injury:Ensuring the patient is properly positioned, padded, and protected from any potential hazards during the procedure.
Post-ECT Interventions
- Monitoring the patient’s recovery:Observing the patient’s vital signs, level of consciousness, and neurological status after the procedure.
- Providing comfort and support:Assisting the patient with pain management, hydration, and any other comfort measures needed during recovery.
- Educating the patient and family:Providing information about the procedure, recovery process, and any potential side effects.
- Assessing the patient’s response to treatment:Monitoring the patient’s progress and making any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan in collaboration with the healthcare team.
Monitoring and Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan For Ect
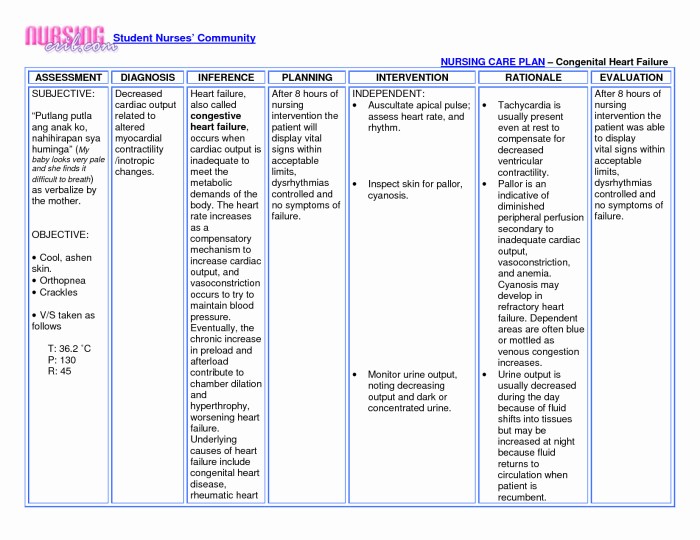
Monitoring and evaluation are crucial aspects of ECT to ensure patient safety, optimize treatment outcomes, and make necessary adjustments. During and after ECT, various parameters are closely monitored to assess the patient’s response and potential complications.
Ongoing evaluation is essential to determine the effectiveness of the treatment plan. It involves regular assessments of the patient’s symptoms, cognitive function, mood, and overall well-being. This ongoing evaluation helps identify any changes or improvements and allows the healthcare team to make informed decisions about continuing or modifying the treatment plan.
Parameters Monitored During and After ECT
- Vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation)
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to monitor heart rhythm
- Oxygen levels
- Cognitive function (memory, attention, orientation)
- Neurological status (pupillary response, reflexes)
- Post-ictal symptoms (confusion, agitation, headache)
- Mood and behavior
Importance of Outcome Measures and Patient Feedback
Outcome measures are essential in evaluating the effectiveness of ECT. These measures include standardized assessment tools, patient-reported outcomes, and clinician observations. By tracking changes in these measures over time, healthcare providers can assess the impact of ECT on the patient’s symptoms and overall functioning.
Patient feedback is also crucial in guiding care. Patients’ subjective experiences, including their perceptions of improvement, side effects, and overall satisfaction with treatment, provide valuable insights that can help tailor the treatment plan to their individual needs.
Patient Education and Support
Patient education and support are crucial throughout the ECT process to ensure informed decision-making, manage expectations, and promote well-being.
The nurse plays a vital role in providing comprehensive information to patients and their families. This includes:
Pre-ECT Information
- Purpose and benefits of ECT
- Procedure details, including risks and side effects
- Expectations during and after ECT
- Consent and decision-making process
Post-ECT Information
- Recovery process and expected side effects
- Medications and follow-up appointments
- Lifestyle adjustments and coping mechanisms
- Support resources and community involvement
The nurse also provides emotional support and coping mechanisms. This may include:
- Active listening and validation of feelings
- Encouraging expression of emotions and concerns
- Teaching relaxation techniques and stress management
- Connecting patients with support groups and resources
Interdisciplinary Collaboration

Interdisciplinary collaboration is crucial for the effective and comprehensive care of patients undergoing electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). A team approach ensures that patients receive the best possible care from a variety of healthcare professionals with specialized expertise.
Key Members of the Interdisciplinary Team
The interdisciplinary team for ECT typically includes:
- Psychiatrist: Responsible for diagnosing the patient’s condition, prescribing ECT, and monitoring its progress.
- Anesthesiologist: Administers anesthesia during ECT procedures and ensures the patient’s safety.
- Nurse: Provides bedside care, monitors the patient’s vital signs, and administers medications.
- Social worker: Assesses the patient’s social and emotional well-being and provides support to the patient and their family.
- Occupational therapist: Helps the patient regain functional abilities and independence after ECT.
Strategies for Effective Communication and Coordination of Care
Effective communication and coordination of care among the interdisciplinary team are essential for ensuring the patient’s safety and well-being. This can be achieved through:
- Regular team meetings to discuss the patient’s progress and any changes in their condition.
- Clear and concise communication channels, such as a shared electronic health record or a dedicated communication platform.
- Established protocols and guidelines for ECT administration and patient care.
- A designated team leader who facilitates communication and ensures that all team members are informed and up-to-date on the patient’s care plan.
By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, healthcare professionals can provide patients with the best possible care, improve outcomes, and reduce the risk of complications.
Nursing care plans for ECT involve assessing and managing risks associated with the procedure. To promote patient well-being, healthcare professionals should consider various aspects, including physical and mental health. A balanced diet rich in fruits, such as those found in frutas de américa del sur , can contribute to overall patient health and recovery.
Understanding these dietary needs is crucial for developing comprehensive nursing care plans for ECT.
Ethical Considerations
ECT is a complex treatment that raises several ethical considerations. These considerations include patient autonomy, informed consent, and the potential for misuse.
The principle of informed consent requires that patients be provided with all the information they need to make an informed decision about whether or not to undergo ECT. This information should include the risks and benefits of ECT, as well as the alternatives to ECT.
Patient Autonomy
Patient autonomy is the right of patients to make decisions about their own healthcare. This right includes the right to refuse treatment, even if the treatment is recommended by a healthcare professional.
In the case of ECT, patients must be given the opportunity to make an informed decision about whether or not to undergo the treatment. This decision should be based on the patient’s understanding of the risks and benefits of ECT, as well as the patient’s own values and preferences.
Nurse’s Role
Nurses play an important role in ensuring that ECT is used ethically and responsibly. Nurses can help to ensure that patients are provided with all the information they need to make an informed decision about ECT.
Nurses can also help to protect patients from the potential misuse of ECT. Nurses can do this by reporting any concerns they have about the use of ECT to the appropriate authorities.
Case Studies and Examples
Case studies and examples can provide valuable insights into the application of the nursing care plan for ECT. They can illustrate the challenges and successes encountered in real-world settings, and help to identify areas for improvement.
One case study involved a patient with severe depression who was unresponsive to medication and psychotherapy. After undergoing a series of ECT treatments, the patient experienced significant improvement in their symptoms and was able to return to work and resume their normal activities.
Challenges
- ECT can be a controversial treatment, and there are ethical concerns about its use.
- ECT can cause side effects, such as memory loss and confusion.
- ECT is not always effective, and some patients may not experience any improvement in their symptoms.
Successes
- ECT can be an effective treatment for severe depression that is unresponsive to other treatments.
- ECT can help patients to return to work and resume their normal activities.
- ECT can improve the quality of life for patients with severe depression.
Areas for Improvement
- More research is needed to better understand the risks and benefits of ECT.
- New methods of administering ECT are being developed to reduce the risk of side effects.
- ECT should be used as a last resort after other treatments have failed.
Future Directions and Research
The field of ECT is constantly evolving, with new research emerging to improve the effectiveness and safety of the procedure. Nurses play a vital role in the care of patients undergoing ECT, and it is essential for them to stay up-to-date on the latest developments in the field.
One of the most promising areas of research is the development of new ECT techniques. These techniques aim to reduce the side effects of ECT, such as memory loss and cognitive impairment. For example, researchers are exploring the use of ultra-brief pulse ECT, which delivers shorter pulses of electricity than traditional ECT.
This technique has been shown to be as effective as traditional ECT, but with fewer side effects.
Another area of research is the development of new methods to monitor the effects of ECT. This is important to ensure that patients are receiving the optimal dose of ECT and that they are not experiencing any adverse effects. For example, researchers are developing new neuroimaging techniques to monitor brain activity during ECT.
This information can be used to tailor the ECT treatment to each individual patient.
Implications for Nursing Practice, Nursing care plan for ect
The findings of research on ECT have important implications for nursing practice. Nurses need to be aware of the latest developments in the field and incorporate them into their care of patients undergoing ECT. For example, nurses should be familiar with the use of ultra-brief pulse ECT and other new ECT techniques.
They should also be able to monitor the effects of ECT and identify any adverse effects.
By staying up-to-date on the latest research on ECT, nurses can help to ensure that patients receive the best possible care.
User Queries
What is the primary goal of a nursing care plan for ECT?
To provide a comprehensive framework for assessing, planning, implementing, and evaluating nursing care for patients undergoing ECT, ensuring their safety, well-being, and optimal outcomes.
What are the key components of a nursing assessment for ECT?
Physical examination, psychological evaluation, social history, and use of standardized assessment tools to gather a thorough understanding of the patient’s condition and needs.
How do nurses monitor patients during and after ECT?
By observing vital signs, neurological status, cognitive function, and overall well-being, ensuring prompt intervention and management of any adverse effects.